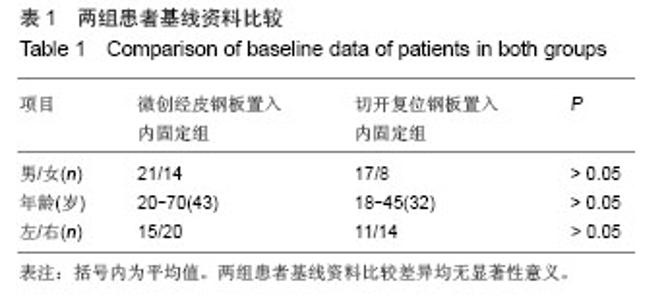
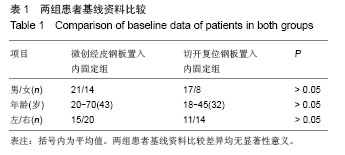
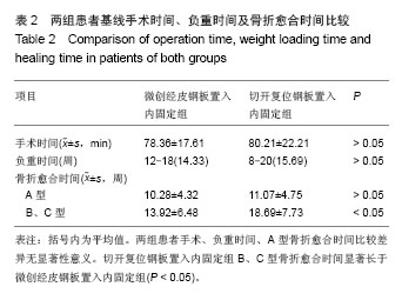
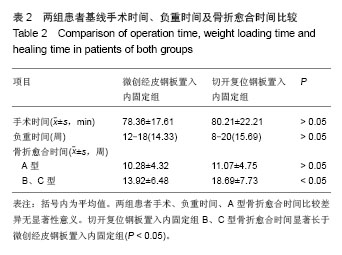
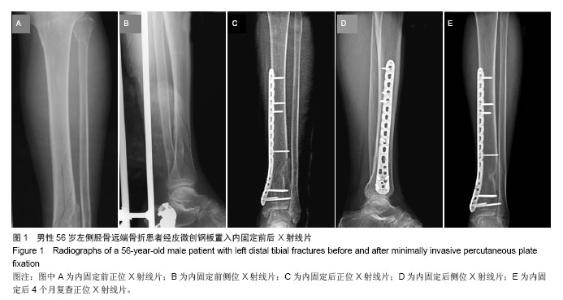
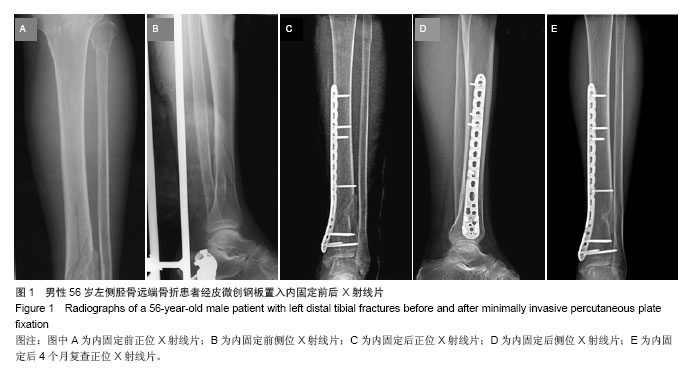
| [1]张发惠,陈振光.胫后血管肌间隙支胫骨内侧骨膜瓣移位术的应用解剖[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,1996,14(4):259-261.
[2]Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJM. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004; 35(6):615-620.
[3]王和鸣,主编.中医伤科学[M].1版.北京:中国中医药出版社,2005: 171-173.
[4]Othman M, Strzelczyk P. Results of conservative treatment of" pilon" fractures. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2003; 5(6): 787-794.
[5]Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2002;84(8): 1093-1110.
[6]Sarmiento A, Latta LL. 450 closed fractures of the distal third of the tibia treated with a functional brace. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;428: 261-271.
[7]Bahari S, Lenehan B, Khan H, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate fixation of distal tibia fractures. Acta Orthopædica Belgica. 2007;73(5): 635.
[8]Frigg R. Locking Compression Plate (LCP). An osteosynthesis plate based on the Dynamic Compression Plate and the Point Contact Fixator (PC-Fix). Injury. 2001;32: 63-66.
[9]Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(5): 307-311.
[10]Kai H, Yokoyama K, Shindo M, et al. Problems of various fixation methods for open tibia fractures: experience in a Japanese level I trauma center. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead, NJ). 1998;27(9): 631-636.
[11]Helfet DL, Koval K, Pappas J, et al. Intraarticular" pilon" fracture of the tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;298: 221-228.
[12]Farouk O, Krettek C, Miclau T, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and vascularity: preliminary results of a cadaver injection study. Injury. 1997;28: A7-A12.
[13]Tornetta III P, Creevy W. Lag screw only fixation of the lateral malleolus. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(2): 119-121.
[14]Carlile GS, Giles NCL. Surgical technique for minimally invasive fibula fracture fixation. Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;17(3): 119-123.
[15]Farouk O, Krettek C, Miclau T, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis: does percutaneous plating disrupt femoral blood supply less than the traditional technique? J Orthop Trauma. 1999;13(6): 401-406.
[16]Helfet DL, Shonnard PY, Levine D, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal fractures of the tibia. Injury. 1997;28: A42-A48.
[17]Kankate RK, Singh P, Elliott DS. Percutaneous plating of the low energy unstable tibial plateau fractures: a new technique. Injury. 2001;32(3): 229-232.
[18]刘志雄.骨科常用诊断分类方法和功能结果评定标准[M]. 北京:北京科学技术出版社,2005:296-297.
[19]Wenda K, Ritter G, Degreif J, et al. Zur genese pulmonaler komplikationen nach marknagelosteosynthesen. Der Unfallchirurg. 1988;91(9): 432-435.
[20]Gerber C, Mast JW, Ganz R. Biological internal fixation of fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;109(6): 295-303.
[21]Palmer RH. Biological osteosynthesis. The Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice. Behavior. 1999; 29(5): 1171-1185.
[22]Krettek C. Foreword: concepts of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury.1997;28 Suppl 1:A1-2.
[23]Rijal L, Sagar G, Mani K, et al. Minimizing radiation and incision in minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) of distal tibial fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(3): 361-365.
[24]Aksekili MAE, Celik I, Arslan AK, et al. The results of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) in distal and diaphyseal tibial fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46(3): 161-167.
[25]钱越宁,胡铁铭,顾宣歆.微创内固定技术治疗胫骨远端粉碎骨折[J].实用骨科杂志, 2008, 14(2): 79-81.
[26]梁博伟,赵劲民,殷国前,等.经皮微创钢板固定治疗胫骨下段骨折:与髓内钉固定和切开复位钢板内固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(17):167-169.
[27]Borrelli Jr J, Prickett W, Song E, et al. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16(10): 691-695.
[28]Giannoudis PV, Schneider E. Principles of fixation of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88(10): 1272-1278.
[29]Sanders R, Haidukewych GJ, Milne T, et al. Minimal versus maximal plate fixation techniques of the ulna: the biomechanical effect of number of screws and plate length. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(3): 166-171.
[30]陈科杰.微创经皮锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗胫骨中下段闭合性骨折疗效观察[J]. 现代实用医学,2013,25(9):990-991.
[31]王成勇,郑玉华,高永知,等.微创经皮锁定加压钢板内固定治疗胫骨中下端骨折的临床应用[J].中外医学研究,2012,10(27):28-29.
[32]Liu YW, Kuang Y, Gu XF, et al. [Close reduction combined with minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis for proximal and distal tibial fractures: a report of 56 patients]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(3):248-251.
[33]Zou J, Zhang W, Zhang CQ. Comparison of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis with open reduction and internal fixation for treatment of extra-articular distal tibia fractures. Injury. 2013;44(8):1102-1106.
[34]Kritsaneephaiboon A, Vaseenon T, Tangtrakulwanich B. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fracture using a posterolateral approach: a cadaveric study and preliminary report. Int Orthop. 2013;37(1):105-111.
[35]Ozkaya U, Parmaksizoglu AS, Gul M, et al. Minimally invasive treatment of distal tibial fractures with locking and non-locking plates. Foot Ankle Int. 2009;30(12):1161-1167. |